Polish engineers in an important European Space Agency mission
The European Space Agency is building a satellite that will allow to study the condition of the Earth`s forests and estimate the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the trees. Polish engineers are working on important components of the device.
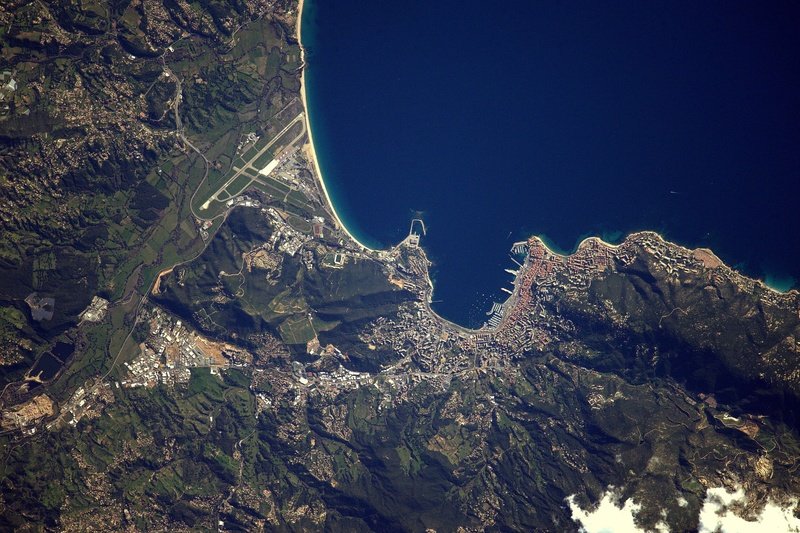
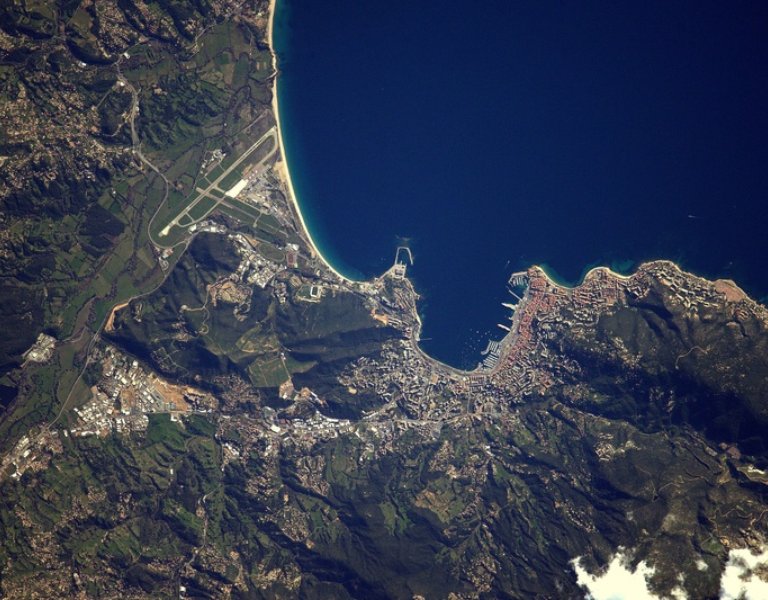
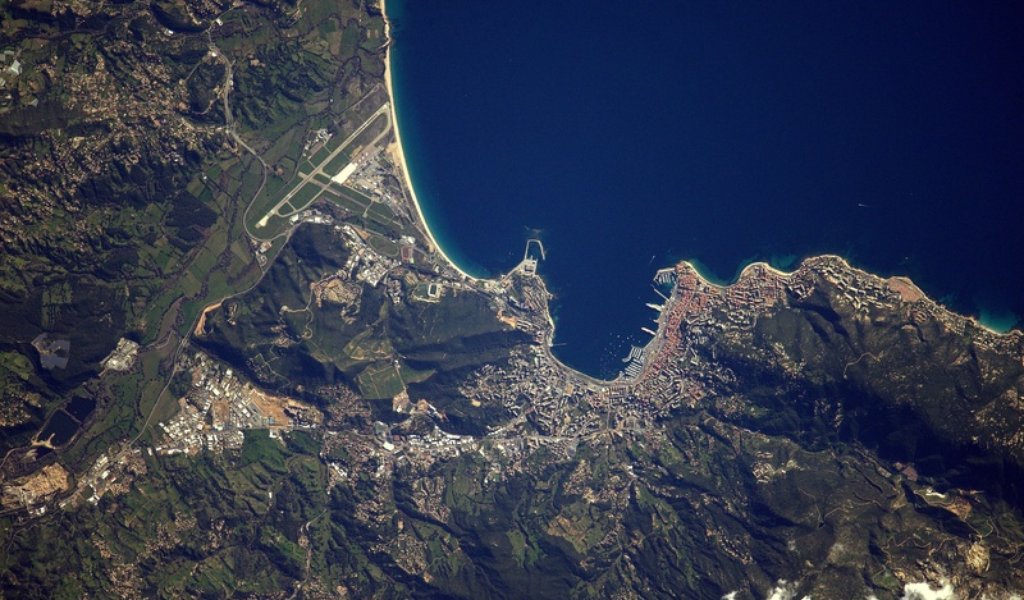
Although few people think about it every day, the trees provide oxygen that we need for breathing, and absorb carbon dioxide. Unfortunately, tropical forests that are called the lungs of the Earth are disappearing at an alarming rate.
Meanwhile, there is no accurate data on the scale of deforestation on the planet. This important information is expected to be provided by the Biomass satellite built as part of the European Space Agency`s mission "Earth Explorer". The device is scheduled to be sent into orbit in 2021 and will operate for 5 years.
Polish specialists participate in the preparation of the mission. The company SENER Polska, commissioned by OHB Italy, will design, manufacture and test devices for the assembly of the satellite structure, including the system for vertical transport, assembly and disassembly of satellite panels, assembly and disassembly of the main research equipment - radar, and a container for the radar transport.
"The objective of this program is finding answers to key scientific questions regarding the environment of our planet" - the company representatives point out.
The data obtained by the satellite are expected to allow to better understand climate change and provide the basis for UN initiatives aimed at reducing carbon emissions caused by deforestation in developing countries.
In order to perform its task, the 20 m long satellite will be equipped with a powerful radar with an antenna with a diameter of 12 m. The waves sent by this device will penetrate dense crowns of trees and scan tree trunks and branches.
As a result, every six months scientists will obtain a precise 3D map of the majority of the world`s forests. It will allow to accurately check the progress of forest losses and estimate the amount of carbon dioxide absorbed by the trees.
But that`s not all. The radar installed on the satellite will also allow to conduct completely different research. For example, archaeologists can use it to search for buildings hidden under the surface of deserts.
The Biomass mission, which has a budget of 420 million euros, is being carried out in cooperation of space agencies from Europe and the U.S.
Source: PAP, Science in Poland
mat/ ekr/ kap/
tr. RL
15.05.2018